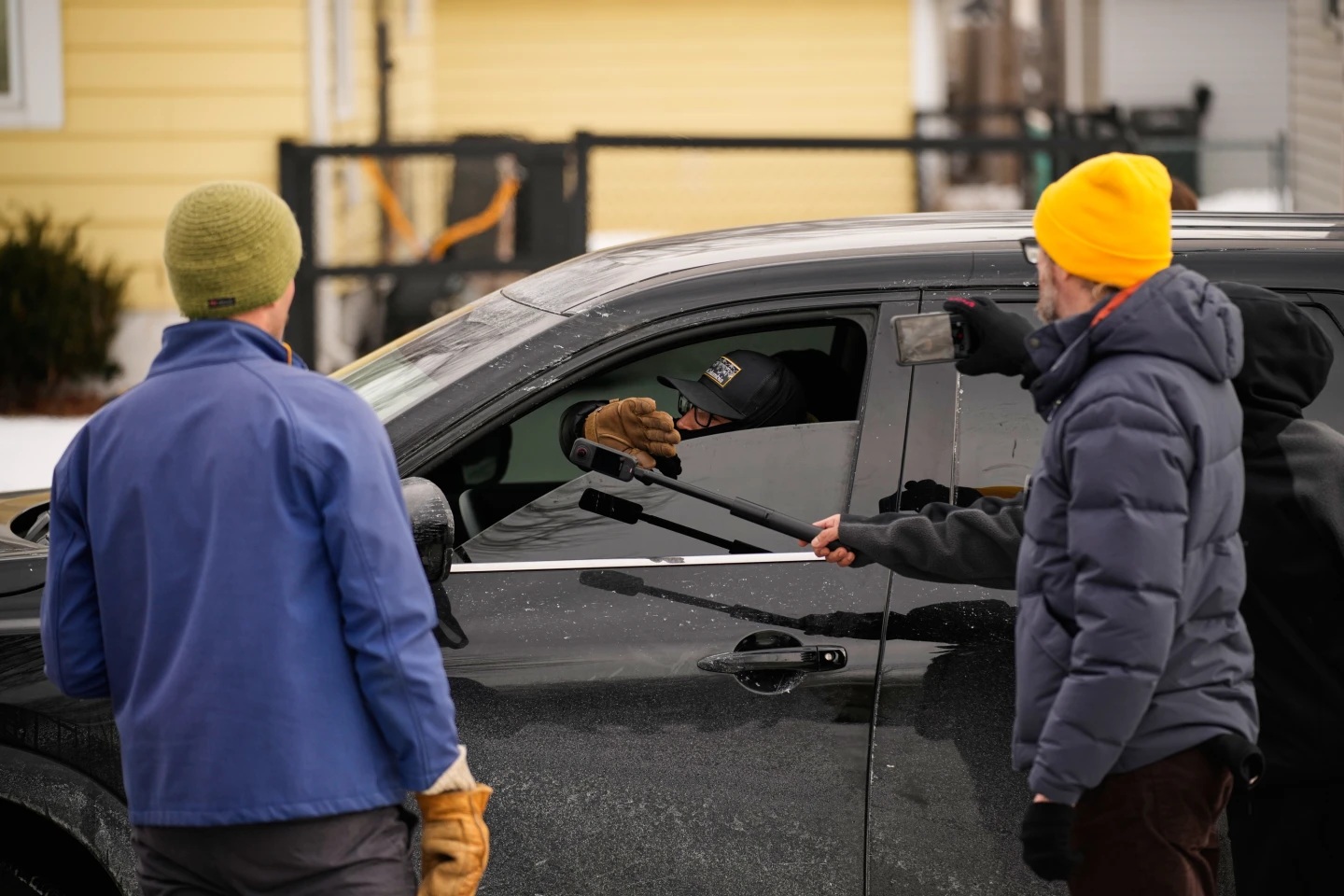
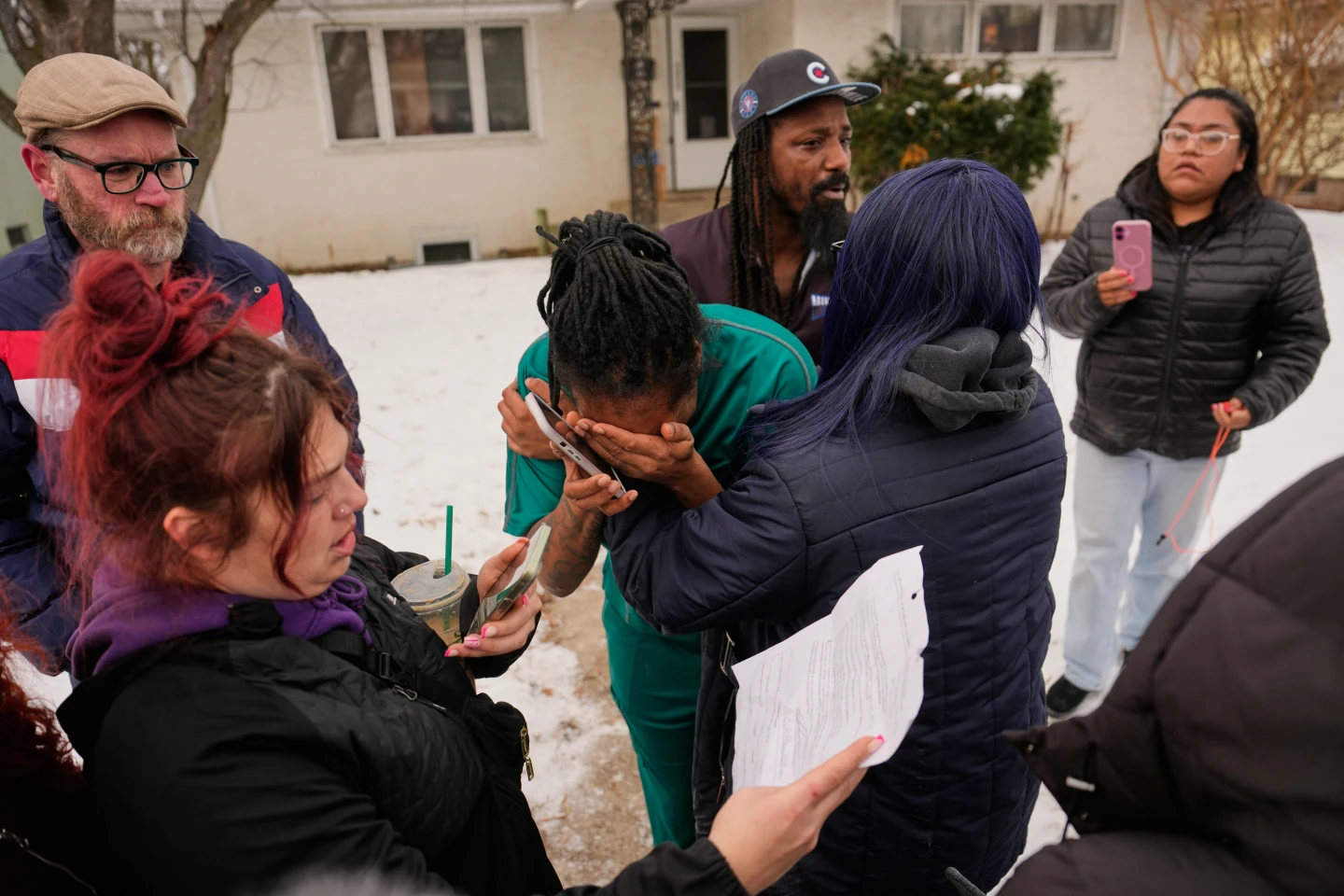As the current administration intensifies its immigration enforcement efforts across the nation, numerous high-profile arrests—many occurring at private residences and businesses, often captured on video—have sparked debates centered on a pivotal legal question: Can federal immigration agents lawfully enter private property to make arrests?
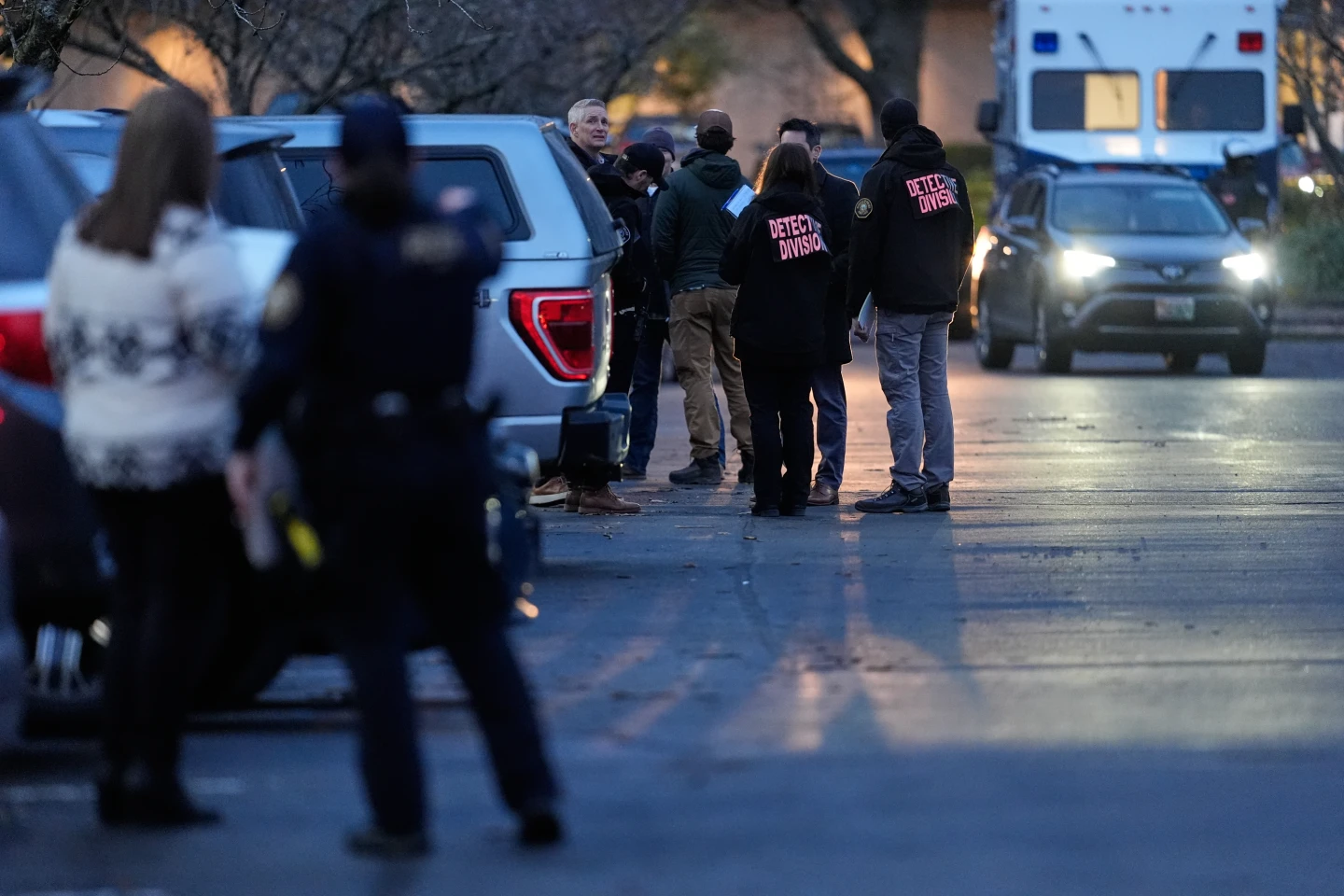
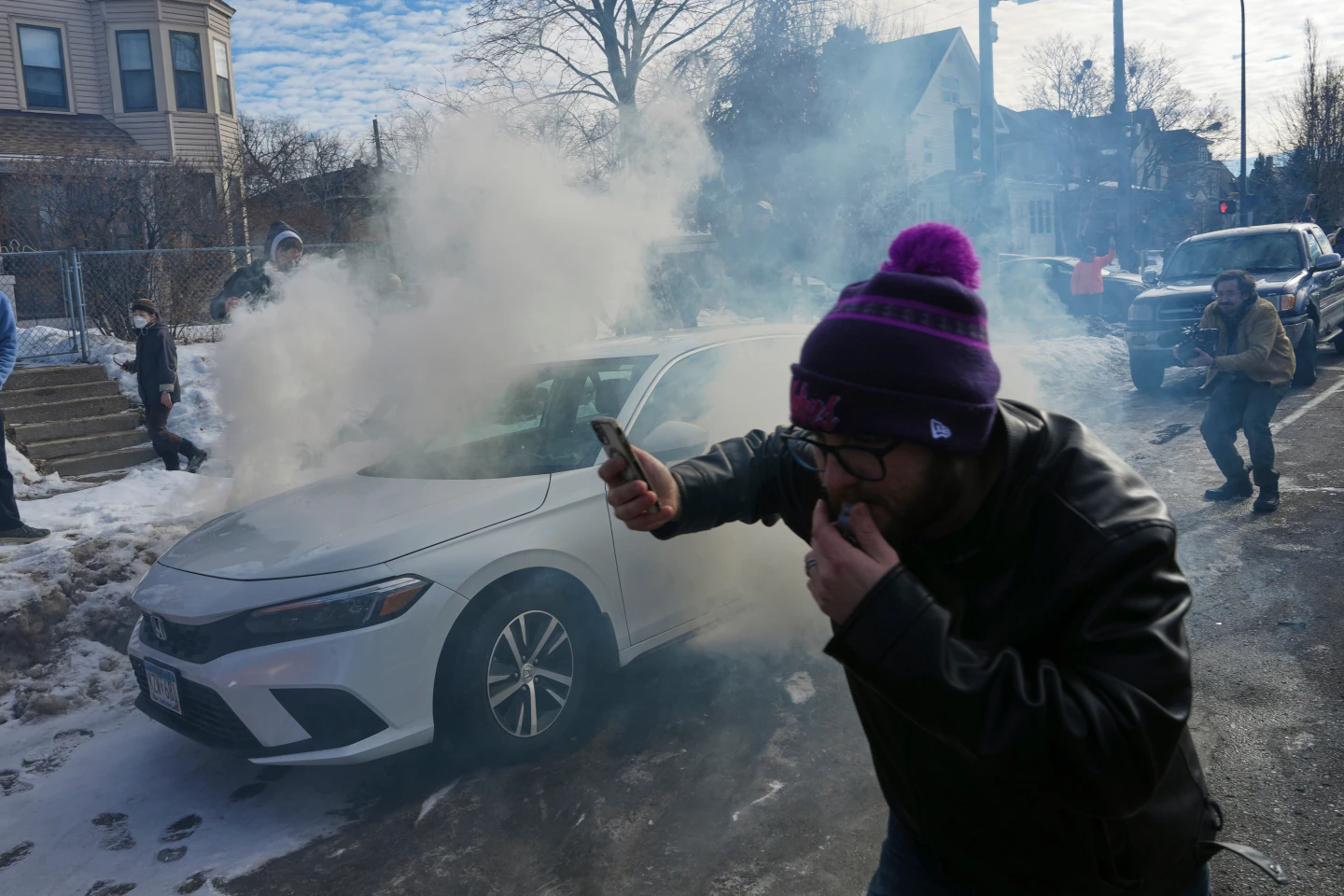
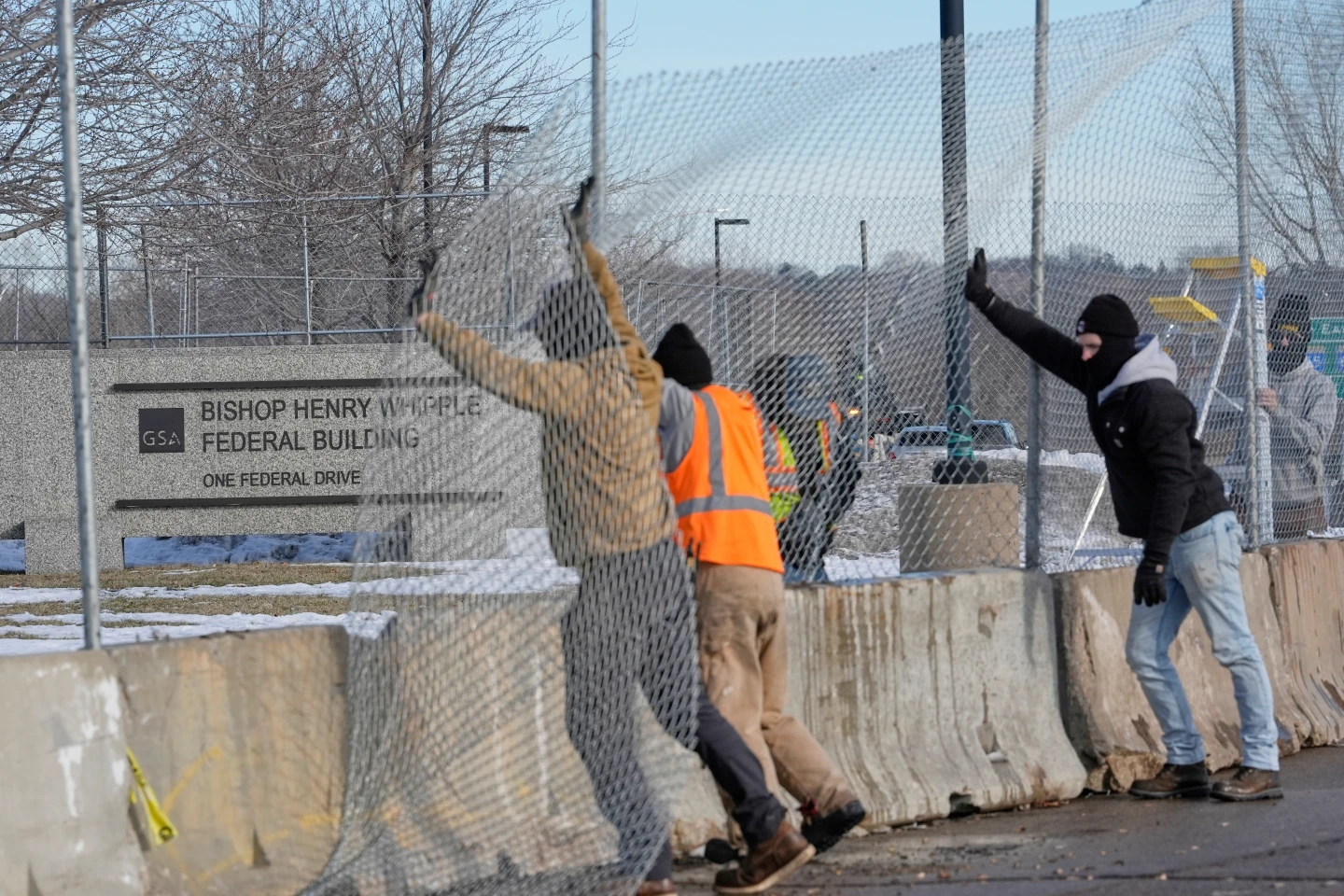
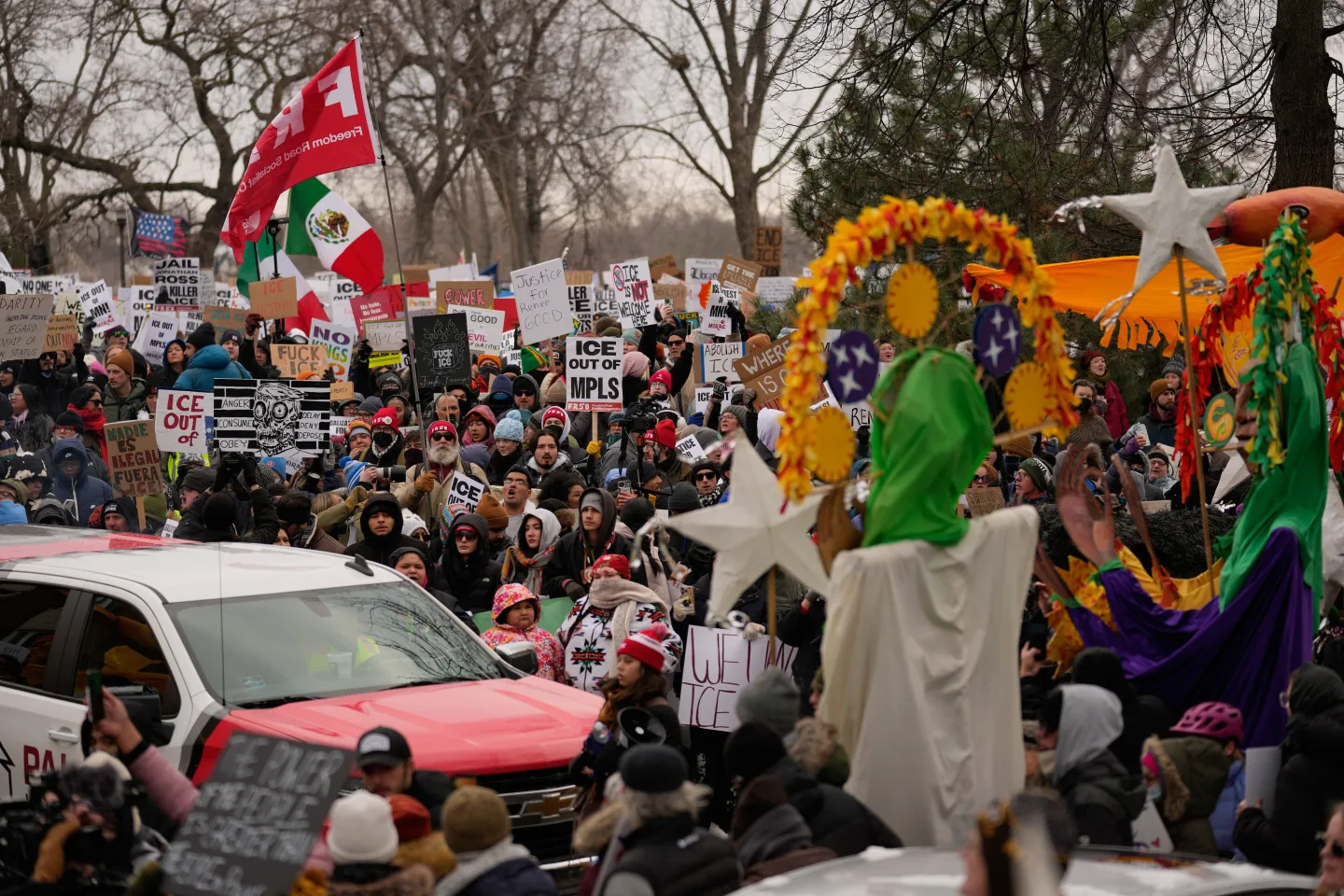
This question has gained urgency in cities such as Minneapolis, where federal agents operate amid a backdrop of protests and tensions, highlighted by recent events infringing on constitutional rights during arrests.
The crux of the debate hinges on a legal distinction that many may not fully understand but is crucial to immigration enforcement practices. Most immigration arrests are conducted under administrative warrants, which are internal documents issued by immigration authorities. These do not grant officers the authority to forcibly enter non-public spaces without consent, unlike judicial warrants, which mandate that an agent can enter private property.
The Legal Framework of Immigration Warrants
All law enforcement actions, including those taken by ICE (Immigration and Customs Enforcement) and CBP (Customs and Border Protection), are governed by the Fourth Amendment, protecting individuals against unreasonable searches and seizures. This constitutionally entrenched protection mandates that officers secure a warrant before searching any private property or arresting someone there, regardless of immigration status.
However, a critical distinction exists between types of warrants. Arrests executed by Homeland Security agencies mainly utilize administrative warrants, as opposed to judicial ones, which are issued by a court and signed by a judge. The latter enables law enforcement to arrest individuals on both public and private property without needing permission.
This distinction becomes even more pertinent when it relates to public awareness and officer training. Former ICE acting director John Sandweg commented on the varying interpretations of entry protocols, emphasizing that as the role of ICE expands, so do the risks of misapplication of these rules.
Recent Cases Highlighting the Issue
The legal challenges surrounding entry without consent were underscored in a recent incident in Minneapolis, where ICE agents reportedly conducted a raid based solely on an administrative warrant. In this situation, no judicial oversight was present, raising serious legal and ethical questions about their actions and the protocols violated.
Despite the contentious nature of such enforcement actions, accountability mechanisms remain vague, as highlighted by the vice president of policy at the National Immigration Law Center, Heidi Altman. She pointed out that while layers of federal laws prohibit inappropriate actions by officers, the federal government often lacks the resolve to impose consequences for breaches of these laws.
Awareness Campaigns and Individual Rights
In response to these enforcement tactics, 'know-your-rights' campaigns aimed at educating individuals about their legal rights in interactions with federal agents have emerged. Such initiatives stress the importance of understanding when and how individuals can refuse entry to agents armed with only administrative warrants, ensuring protections against unauthorized entries.
Activists and legal groups are working across the nation to equip residents with crucial knowledge about their rights, helping to navigate the challenging landscape of immigration law enforcement. They encourage community members to demand warrants before allowing entry and to understand that consent can be lawfully withdrawn when only an administrative warrant is presented.